Introduction to Osteodystrophy and Osteomalacia
Osteodystrophy and osteomalacia may sound like similar conditions, but they are actually quite different when it comes to their causes, symptoms, and treatments. In this article, we will delve into the distinct characteristics of these two bone disorders and help you understand the differences between them. By the end of this article, you will be better equipped to identify the signs of these conditions and seek appropriate treatment if needed.
Understanding Osteodystrophy: Causes and Symptoms
Osteodystrophy is a term used to describe a group of bone disorders that can result from various underlying conditions, such as kidney disease, hormonal imbalances, or genetic disorders. The primary cause of osteodystrophy is the disruption of normal bone metabolism, which can lead to abnormal bone growth, deformities, and fractures. Some common symptoms of osteodystrophy include bone pain, muscle weakness, and growth retardation in children. In severe cases, the condition can result in skeletal deformities, such as bowed legs or an abnormal curvature of the spine.
Understanding Osteomalacia: Causes and Symptoms
On the other hand, osteomalacia refers specifically to a softening of the bones due to a lack of mineralization. This condition is most often caused by a deficiency in vitamin D, which is essential for the proper absorption of calcium and phosphate in the body. Other possible causes of osteomalacia include certain medications, gastrointestinal disorders, and kidney or liver diseases. The most common symptoms of osteomalacia include widespread bone pain, muscle weakness, and an increased risk of fractures. In some cases, osteomalacia can also lead to difficulty walking or moving due to the weakened bones and muscles.
Diagnosing Osteodystrophy and Osteomalacia
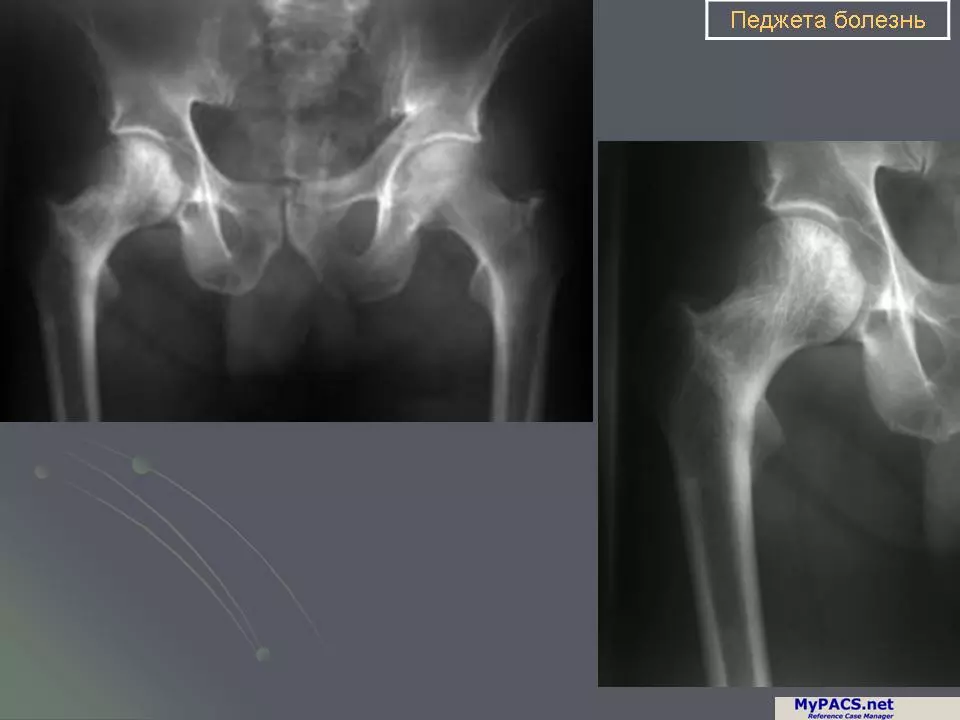
Since the symptoms of osteodystrophy and osteomalacia can overlap, it is crucial to obtain an accurate diagnosis to determine the appropriate course of treatment. Diagnostic tests for both conditions may include blood tests to check for abnormal levels of calcium, phosphorus, and vitamin D, as well as imaging studies like X-rays or bone scans to assess the structure and density of the bones. In some cases, a bone biopsy may be necessary to confirm the diagnosis and rule out other potential causes of bone pain or deformity.
Treatment Options for Osteodystrophy
The treatment for osteodystrophy will largely depend on the underlying cause of the disorder. In cases where kidney disease is the primary cause, treatment may involve dialysis or a kidney transplant to improve the overall function of the kidneys. Hormonal imbalances may be treated with hormone replacement therapy, while genetic disorders may require more specialized treatments. Additionally, addressing any nutritional deficiencies, such as low levels of calcium or vitamin D, can help improve bone health and alleviate some of the symptoms of osteodystrophy.
Treatment Options for Osteomalacia
Since vitamin D deficiency is the most common cause of osteomalacia, treatment typically involves increasing the intake of vitamin D through diet, supplements, or exposure to sunlight. In cases where vitamin D deficiency is caused by a gastrointestinal disorder or another underlying condition, treating the primary cause is essential to resolve the symptoms of osteomalacia. In severe cases, doctors may prescribe high-dose vitamin D supplements or even administer the vitamin through injections to quickly increase the levels of vitamin D in the body.
Preventing Osteodystrophy and Osteomalacia
While it may not be possible to prevent all cases of osteodystrophy and osteomalacia, there are steps you can take to reduce your risk of developing these conditions. Maintaining a healthy, balanced diet that is rich in calcium, phosphorus, and vitamin D can help support strong bones and prevent deficiencies that can contribute to these disorders. Regular exercise, especially weight-bearing activities like walking or jogging, can also help improve bone density and reduce the risk of fractures. Finally, getting regular check-ups and screenings for underlying health conditions can help detect and treat any potential causes of osteodystrophy or osteomalacia before they lead to more severe complications.
Conclusion: Understanding the Differences Between Osteodystrophy and Osteomalacia
In conclusion, while osteodystrophy and osteomalacia may share some similarities in terms of their symptoms and effects on bone health, it is important to recognize the distinct differences between these two conditions. Osteodystrophy is a broader term that encompasses a variety of bone disorders with different underlying causes, while osteomalacia specifically refers to a softening of the bones due to a lack of proper mineralization. Understanding these differences can help you recognize the signs of each condition and seek appropriate treatment to maintain strong, healthy bones throughout your life.



Comments (20)