SSRIs: What They Are, How They Work, and What You Need to Know
When doctors prescribe an antidepressant, SSRIs, a class of medications that increase serotonin levels in the brain to improve mood. Also known as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, they’re among the most commonly used treatments for depression, anxiety, and some OCD cases. Unlike older antidepressants, SSRIs tend to have fewer side effects and are safer in overdose—why so many people start with them.
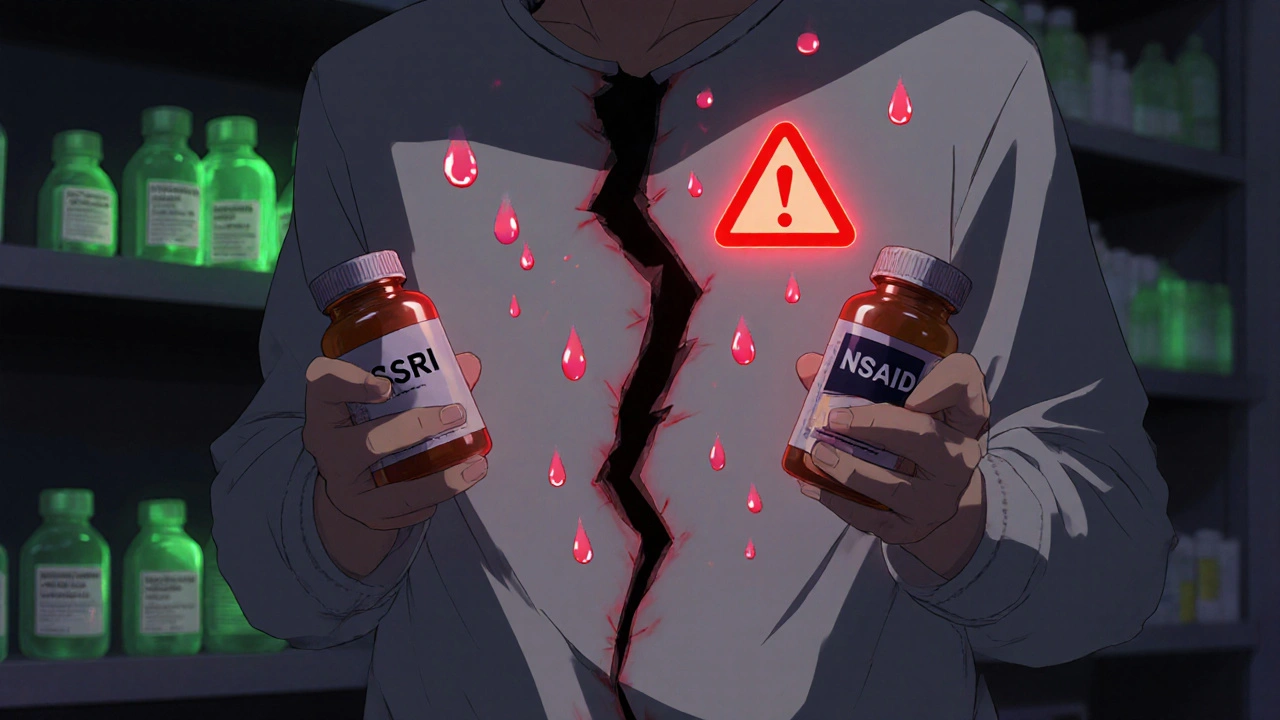
But SSRIs aren’t all the same. Sertraline, a widely prescribed SSRI, can interact with blood thinners, NSAIDs, and even alcohol, raising the risk of bleeding or serotonin syndrome. Vilazodone, another antidepressant that works like an SSRI but also affects other brain receptors, gets mixed up with pure SSRIs even though it’s not one. People often assume all antidepressants behave the same, but that’s not true. Taking sertraline with warfarin? You’re adding risk. Mixing vilazodone with other mood drugs? Could trigger serotonin syndrome—a rare but dangerous condition with high fever, confusion, and rapid heart rate.
What you’ll find below isn’t just a list of articles. It’s a practical guide to what really matters when you’re on or considering SSRIs: drug interactions, side effects, how they compare to other meds, and what to watch for. You’ll see real details on sertraline’s risks, how vilazodone stacks up, and why some people need to switch meds entirely. No fluff. No theory. Just what you need to stay safe and make smarter choices.